Overview
Point in Time Recovery (PITR) allows users to restore documents to a specific state at a given timestamp. This is useful for recovering accidental modifications or deletions, maintaining data integrity, and providing historical traceability.
Cloud Firestore PITR keeps versions of documents for up to 7 days. It does not impact performance for databases following best practices.
How It Works
PITR maintains historical snapshots of documents. You can pick a specific timestamp to view and restore data as it was at that moment.
PITR Window
- Data is retained for 7 days after enabling PITR.
- Earliest PITR availability:
- PITR disabled: Data is available 1 hour before the read request.
- Enabled within 7 days: Data is available 1 hour before enabling PITR.
- Enabled over 7 days ago: Data is available 7 days before the read request.
- One version per minute is kept. Only the latest version per minute is stored if multiple writes occur.
- Non-minute granular reads (e.g., including milliseconds) return an error.
- The
earliestVersionTimefield indicates the earliest recoverable timestamp.
Using PITR from the Document Context Menu
This is the most direct way to restore a single document:
1. Accessing PITR
- Navigate to the document list in the database viewer.
- Locate the document to restore.
- Right-click or open the contextual menu and select Point in Time Recovery.
2. Selecting a Version
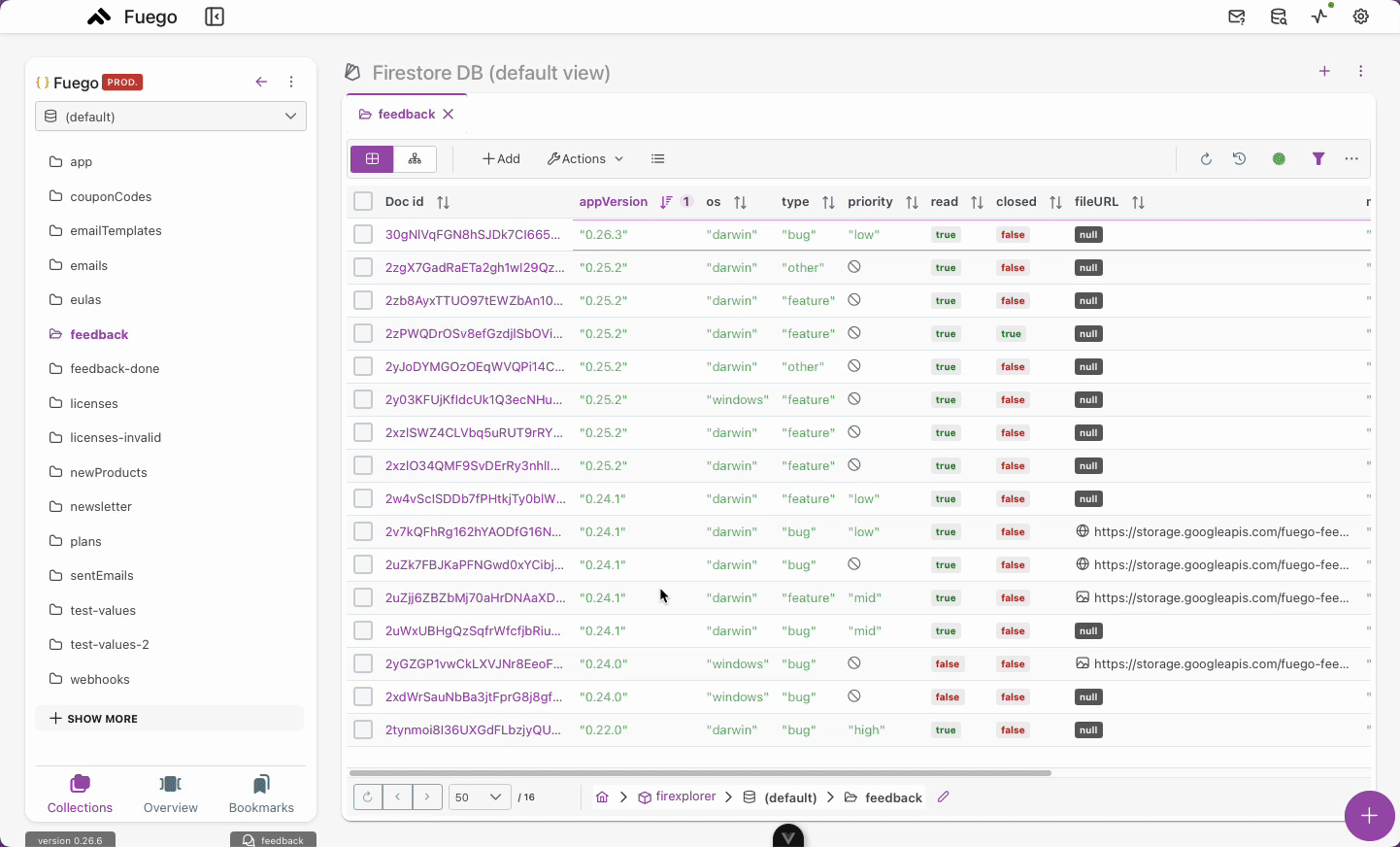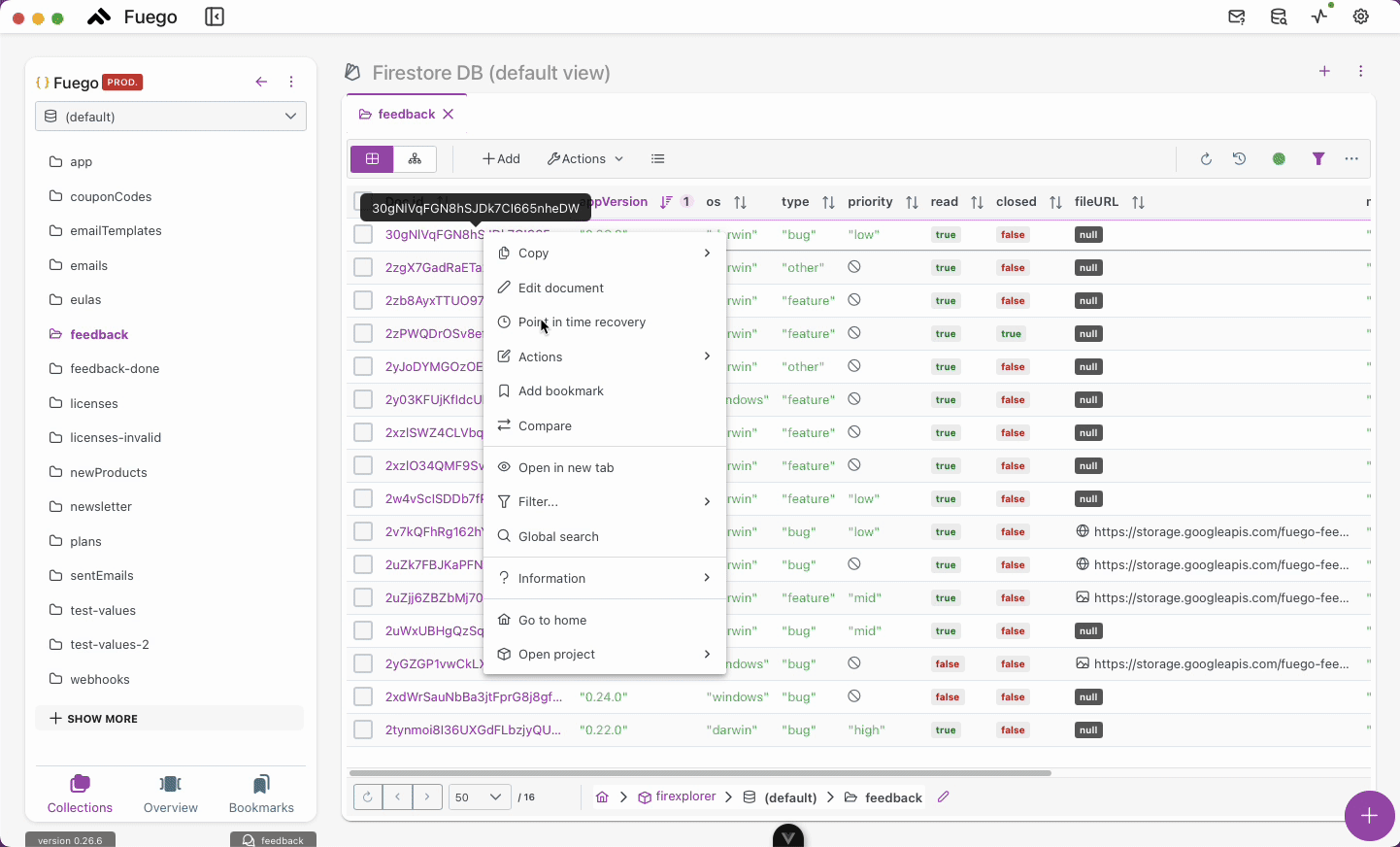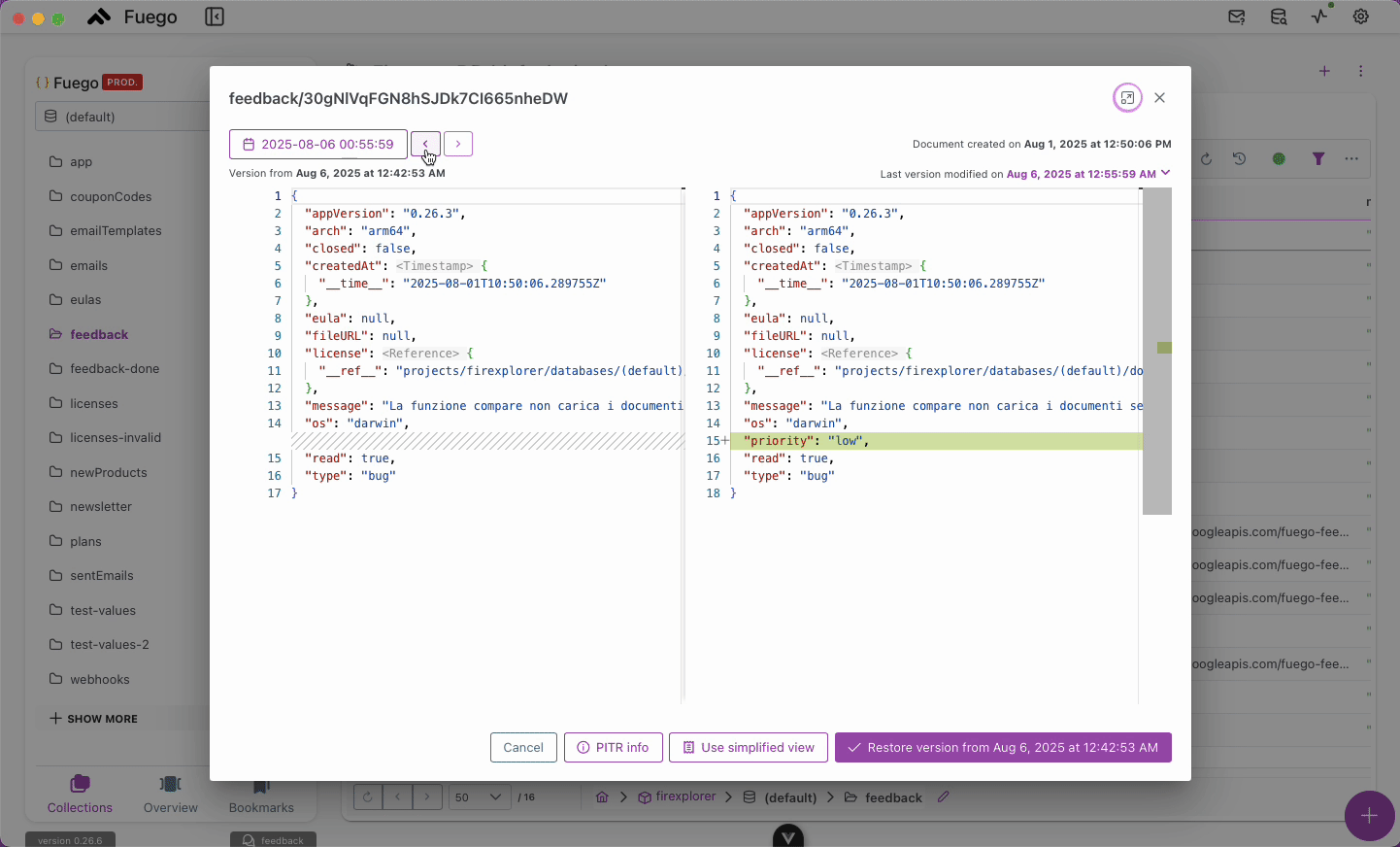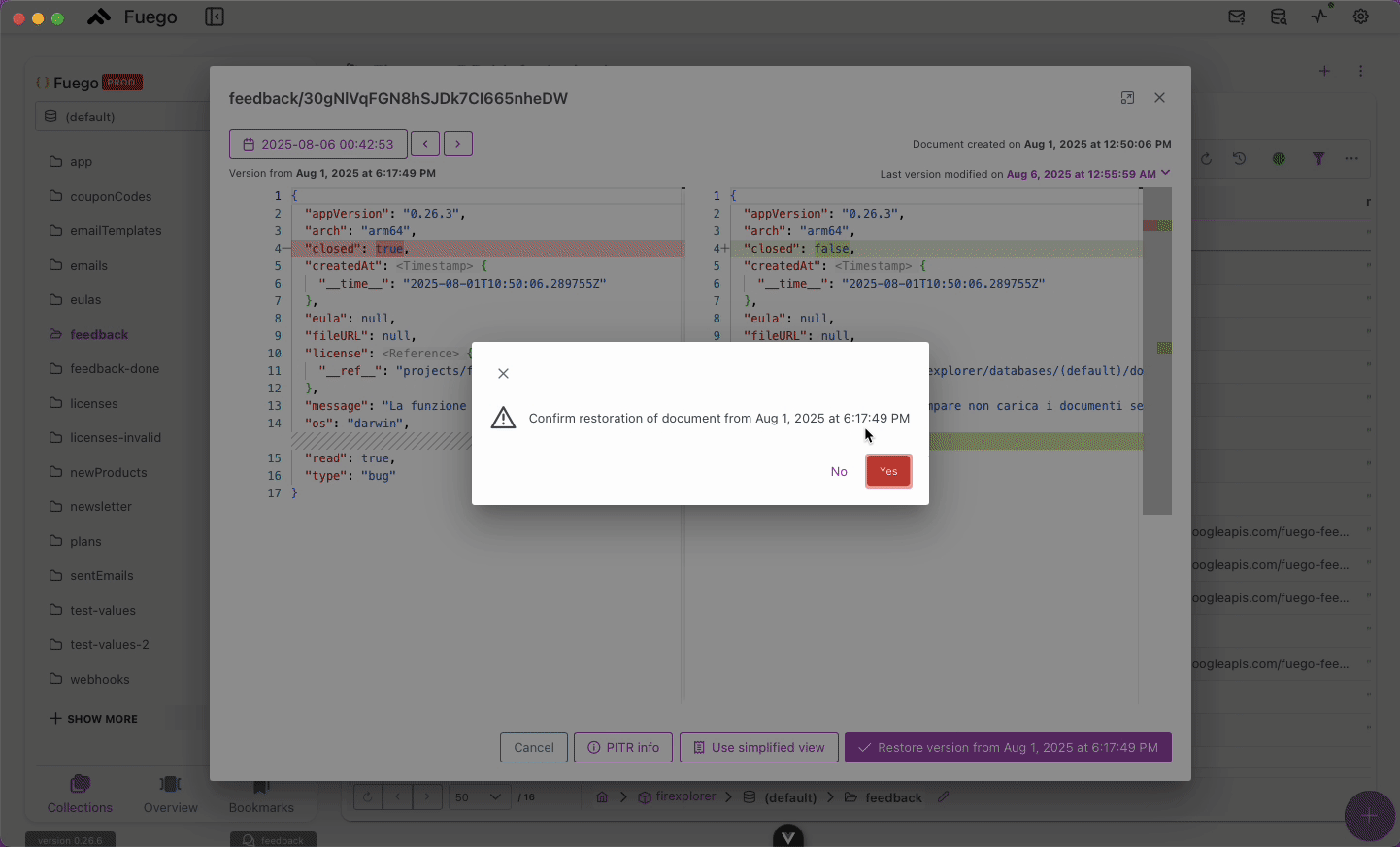
- A history panel appears showing available snapshots.
- Select the timestamp to view that version.
- Compare the current document with the historical version.
3. Restoring a Version
- Click Restore version.
- Confirm the action.
- The document reverts to that state, and the audit log preserves the change.
Using PITR with Query Read-Time
This method is useful for bulk review and restoration of multiple documents:
1. Setting a Read-Time
- Open the Firestore DB view.
- Set the read-time for the query to the desired timestamp.
- The interface will show documents as they existed at that point in time.
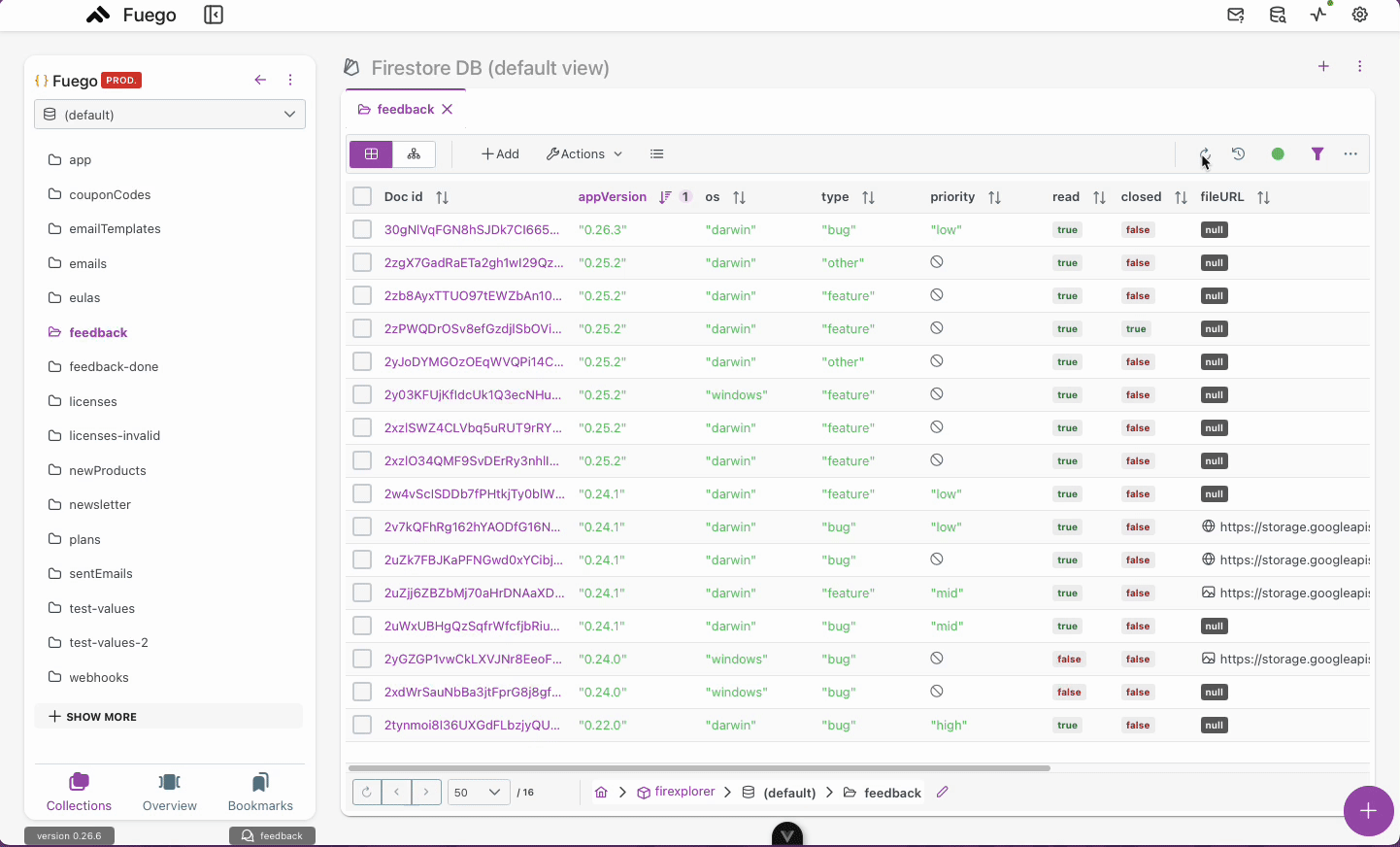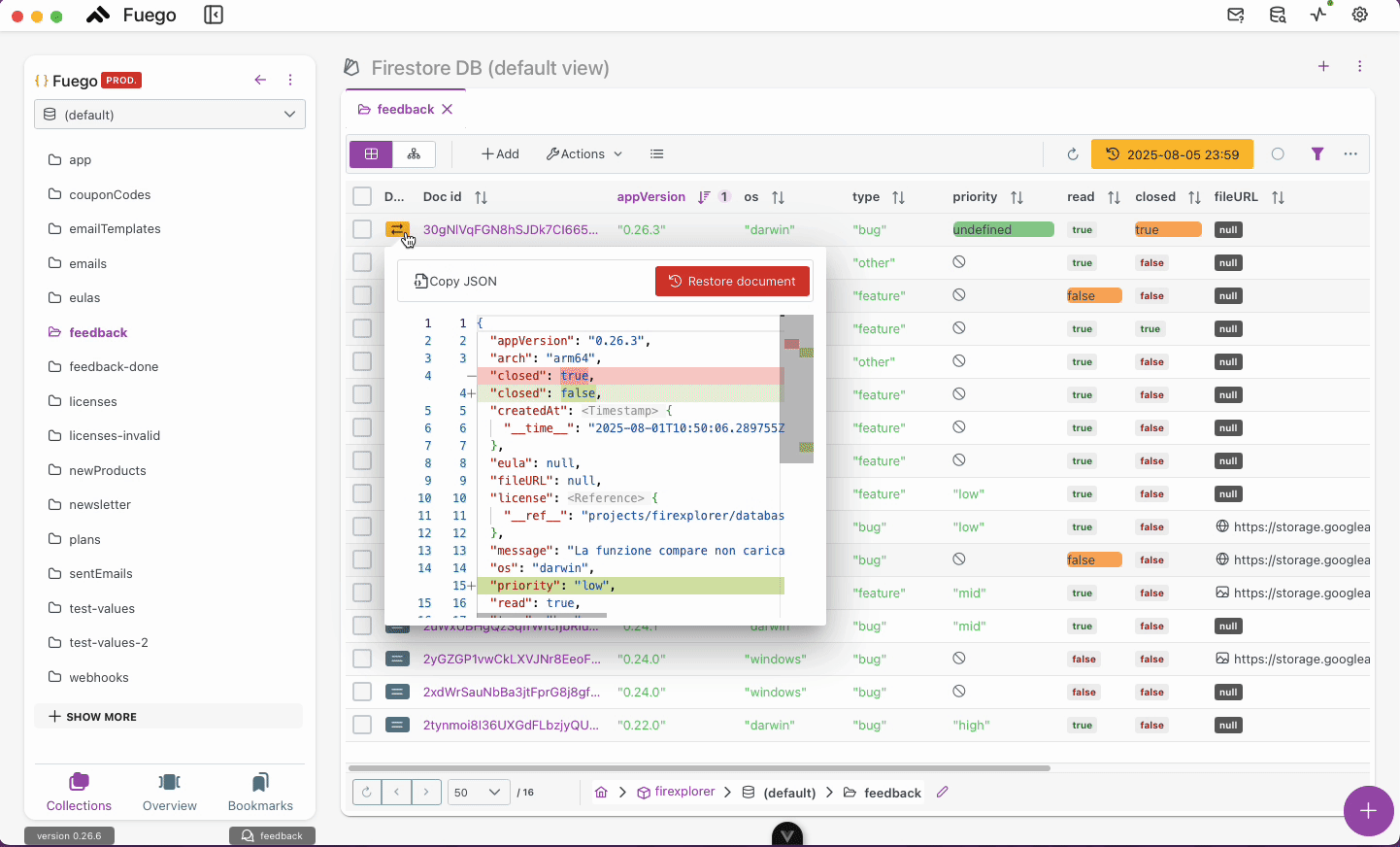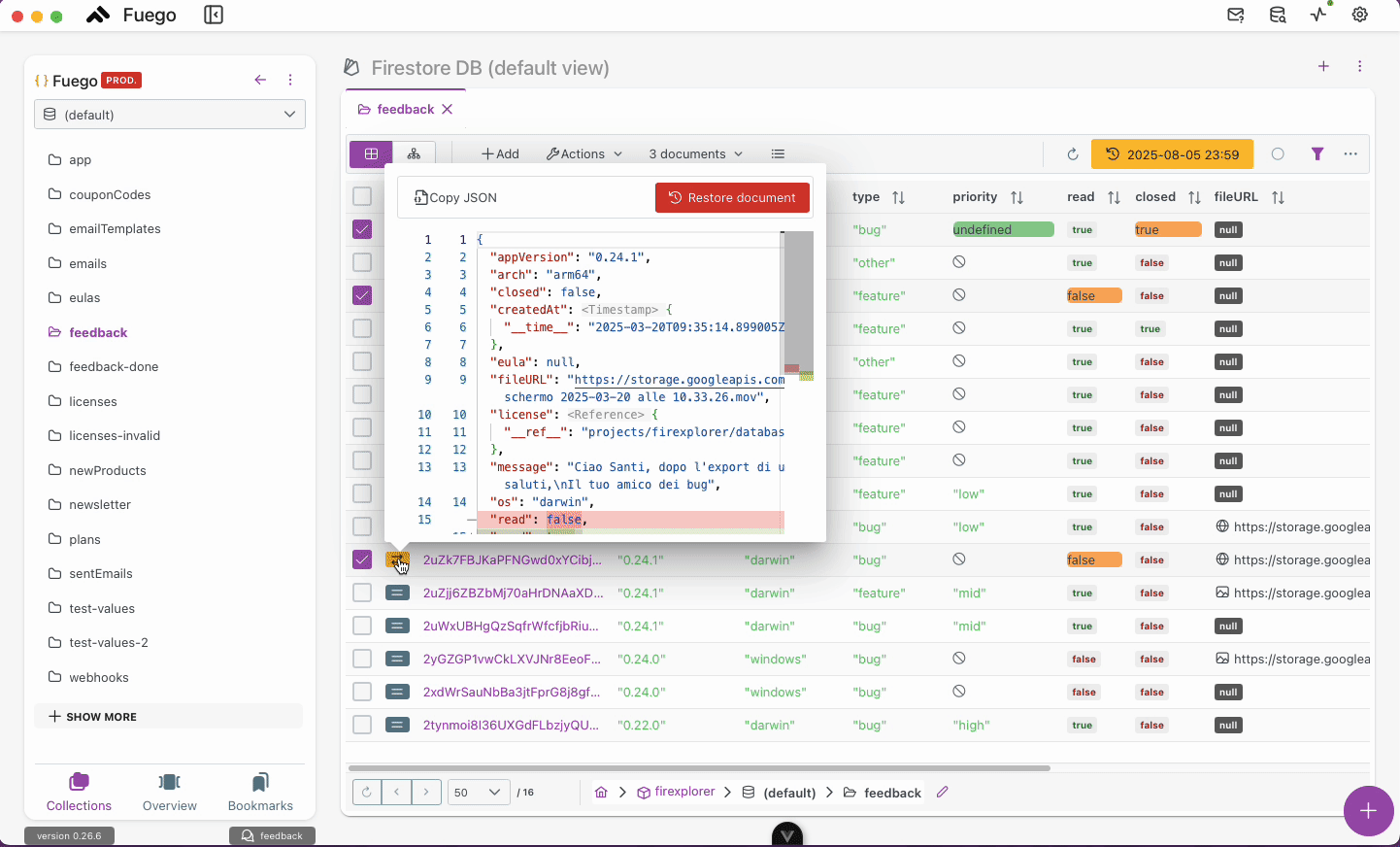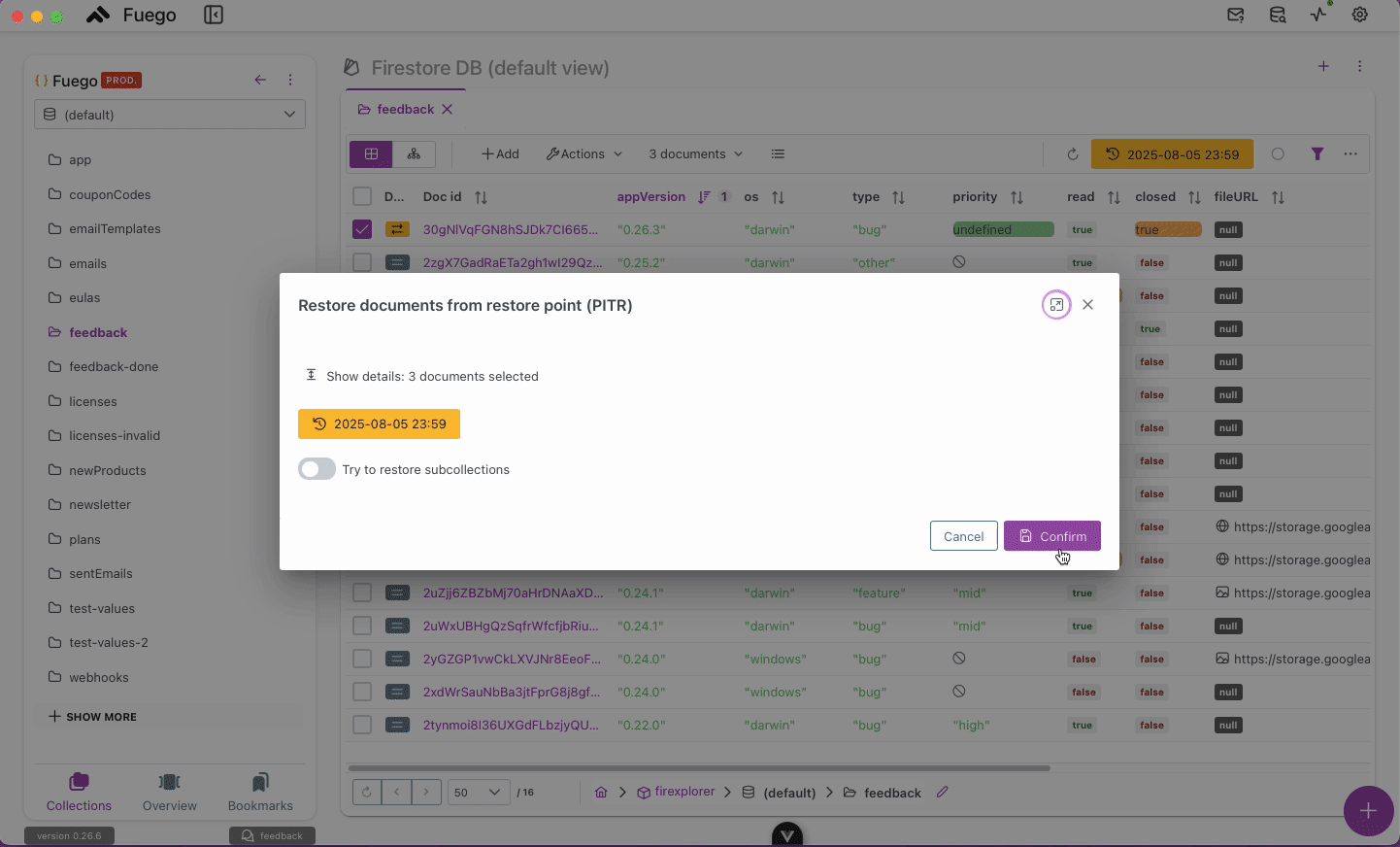
2. Comparing and Selecting Documents
- You can review changes by comparing each document with its current version.
- Select one or multiple documents that you want to restore.
3. Bulk Restoration
- After selecting the documents, choose Restore Selected.
- Confirm the restoration to revert all selected documents.
Common Features
- Granular recovery: Restore documents to a precise timestamp.
- Version comparison: Compare current and historical versions before restoring.
- Data integrity: Previous versions remain available for audits.
- Retention window: Data is stored at minute-level granularity for 7 days.
Best Practices
- Enable PITR before relying on historical recovery.
- Use read-time queries for auditing or batch recovery.
- Compare versions to ensure no critical data is lost before restoring.
- Use minute-granularity timestamps for past reads.
